Particulate model of matter
In this chapter, I gained a deeper understanding of the three states of matter.
All matter of every state is made up of particles that are in constant and random movement. Solid state
 Solids have fixed volume and shape.
Solids have fixed volume and shape.- Solids cannot be compressed.
- Solids are made up of particles that are arranged in a regular pattern where they are very closely packed together and are very strongly attracted to each another.
- Solid particles can only vibrate lightly at their fixed positions.
 Liquids have fixed volumes but do not have a fixed shape.
Liquids have fixed volumes but do not have a fixed shape.- Liquids cannot be compressed.
- Liquids are made up of particles that are packed closely together in a random manner which are also attracted to each another.
- Liquid particles can move over a short distance.
Gaseous state
 Gases do not have fixed volumes and shape.
Gases do not have fixed volumes and shape.- Gases can be compressed.
- Gases are made up of particles that are far apart from one another as they are weakly attracted to one another.
- Gas particles can move about freely in any way.
- When a solid is heated,the particles will then gain energy.
- They start to vibrate more vigorously.
- When the temperature reaches the melting point, the particles will then break free from one another and start moving freely as enough energy is gained.
- The change in movement and arrangement of the particles from the solid to liquid state is called melting.
- When liquid is heated,the particles will then gain energy.
- They start to vibrate more vigorously.
- When the temperature reaches the boiling point, the particles will then break free from one another and become very far apart, moving randomly at high speeds as enough energy is gained.
- The change in movement and arrangement of the particles from the liquid to gaseous state is called boiling.
Freezing
- When liquid is cooled,the particles will then lose energy.
- They start to vibrate less vigorously and slowly.
- When the temperature decreases to the freezing point, the particles will then be attracted to one another again, back to their fixed positions and as energy is lost.
- The change in movement and arrangement of the particles from the liquid to solid state is called freezing.
- When liquid is cooled,the particles will then lose energy.
- They start to vibrate less vigorously and slowly.
- When the temperature decreases to a certain point, the particles will then be attracted to one another again and as certain amount of energy is lost.
- The change in movement and arrangement of the particles from the gaseous to liquid state is called condensation.
Sublimation - change of state from solid to gas, bypassing the liquid state
- When a solid is heated,the particles will then gain energy.
- They start to vibrate very vigorously.
- When the temperature reaches a certain temperature, the particles will then break free from one another and start moving freely, randomly very far apart at great speeds as enough energy is gained.
- The change in movement and arrangement of the particles from the solid to gaseous state is called sublimation.
Heating curve
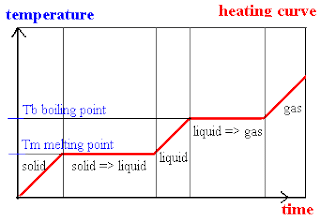 There is a period whereby the temperature stays constant at the boiling and melting points. This is because the heat energy gained at that period is converted to kinetic energy to overcome the forces of attraction holding the particles together. Thus, when enough heat energy is converted to kinetic energy, all the particles would have already broke free from one another, causing temperature wll start rising again
There is a period whereby the temperature stays constant at the boiling and melting points. This is because the heat energy gained at that period is converted to kinetic energy to overcome the forces of attraction holding the particles together. Thus, when enough heat energy is converted to kinetic energy, all the particles would have already broke free from one another, causing temperature wll start rising again Cooling curves
There is a period whereby the temperature stays constant at the freezing point and condensation. The particles slows down as kinetic energy is lost over this short period and the particles starts to attract one another again. Then, the particles will change from the liquid state to solid state of from the gaseous to liquid state. The temperature starts to fall when all particles are in their original positions.
done by: Ng Li Xian
source:

No comments:
Post a Comment